Design, Simulate, Innovate
Turn your concepts into reality with precision, speed, and confidence. Our simulation-driven engineering solutions help you design smarter, perform better, and stay ahead of the competition.






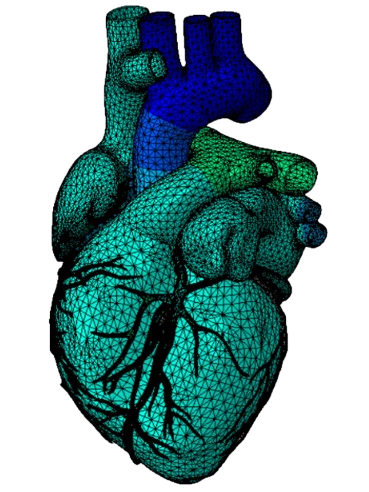
What We Do
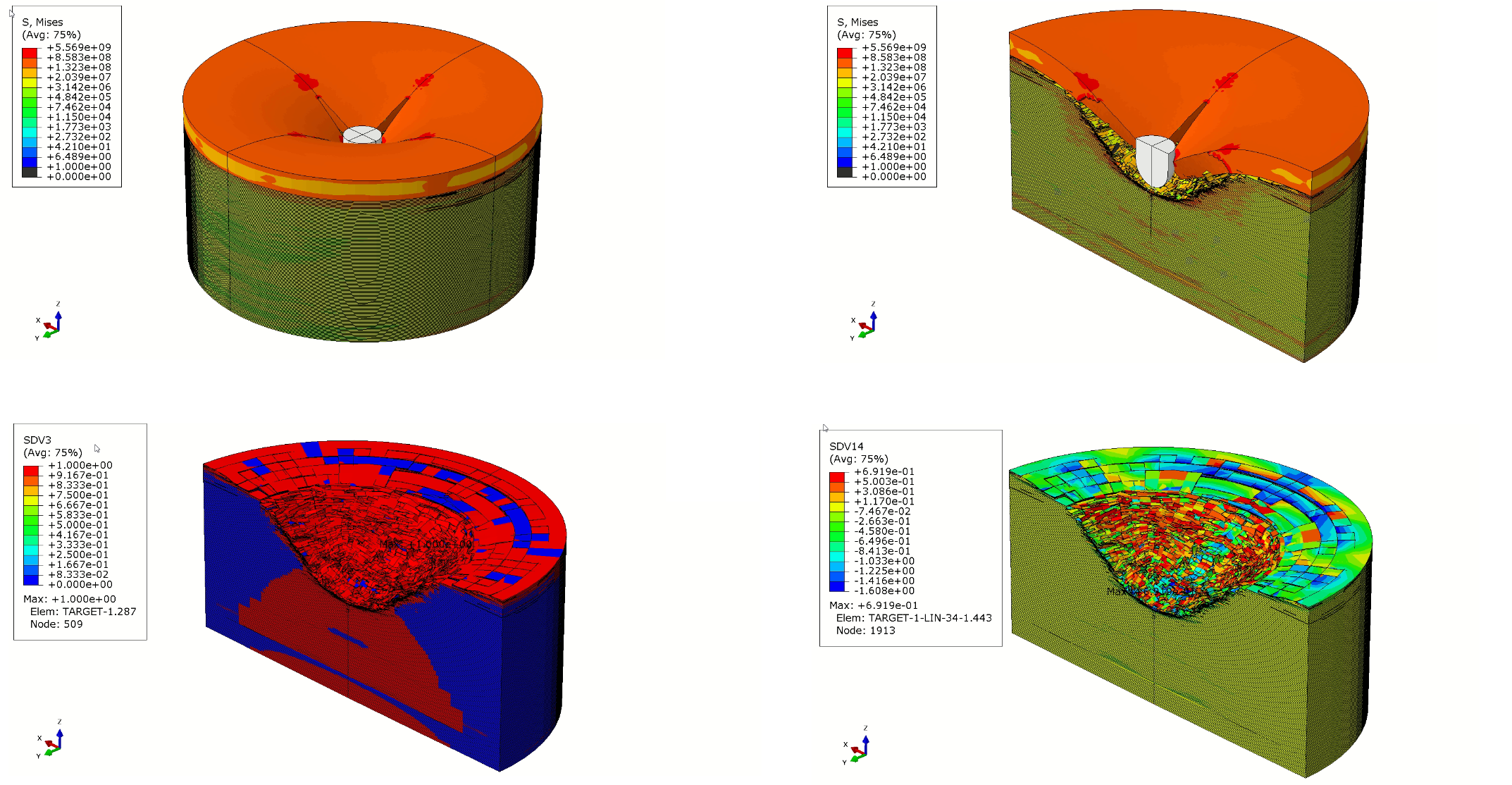
- Linear and non-linear analysis
- User Subroutine
- Composite modelling
- Biomedical application
- Structural modelling
- Geotechnical Application
- Additive Manufacturing
- Welding analysis
- Piezoelectric Modelling
- Polymer analysis
- Machining operation
- Concrete analysis
- Heat transfer analysis
- Low cycle fatigue assessment
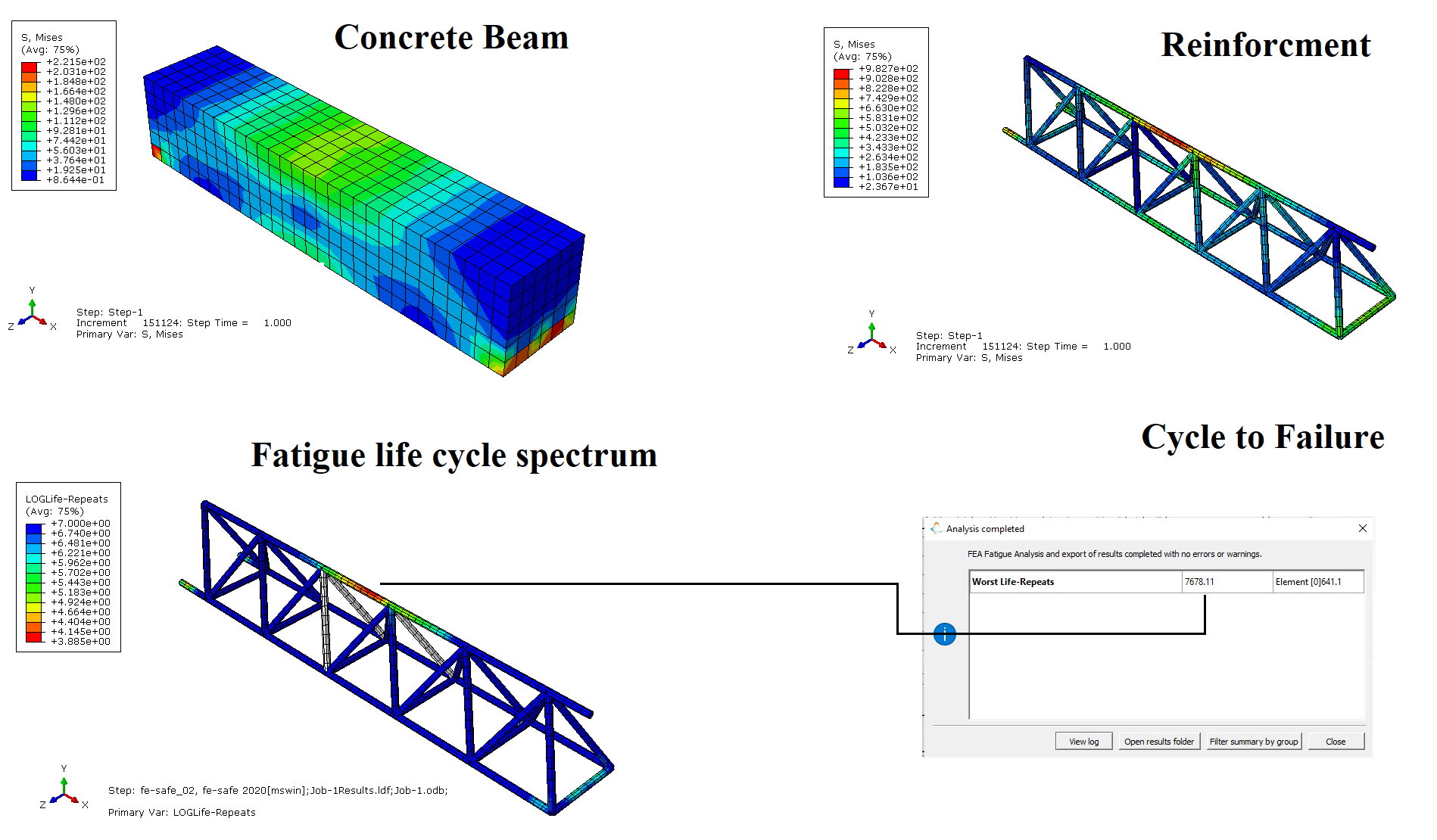
- High cycle Fatigue modelling
- Uni-axial stress based approach
- S-N curve prediction
- Multi-axial stress life approach
- Low cycle Fatigue modelling
- Uni-axial strain based approach
- Multi-axial strain life approach
- Mean stress correction
- Weibull distribution factor
- Fatigue failure Probability
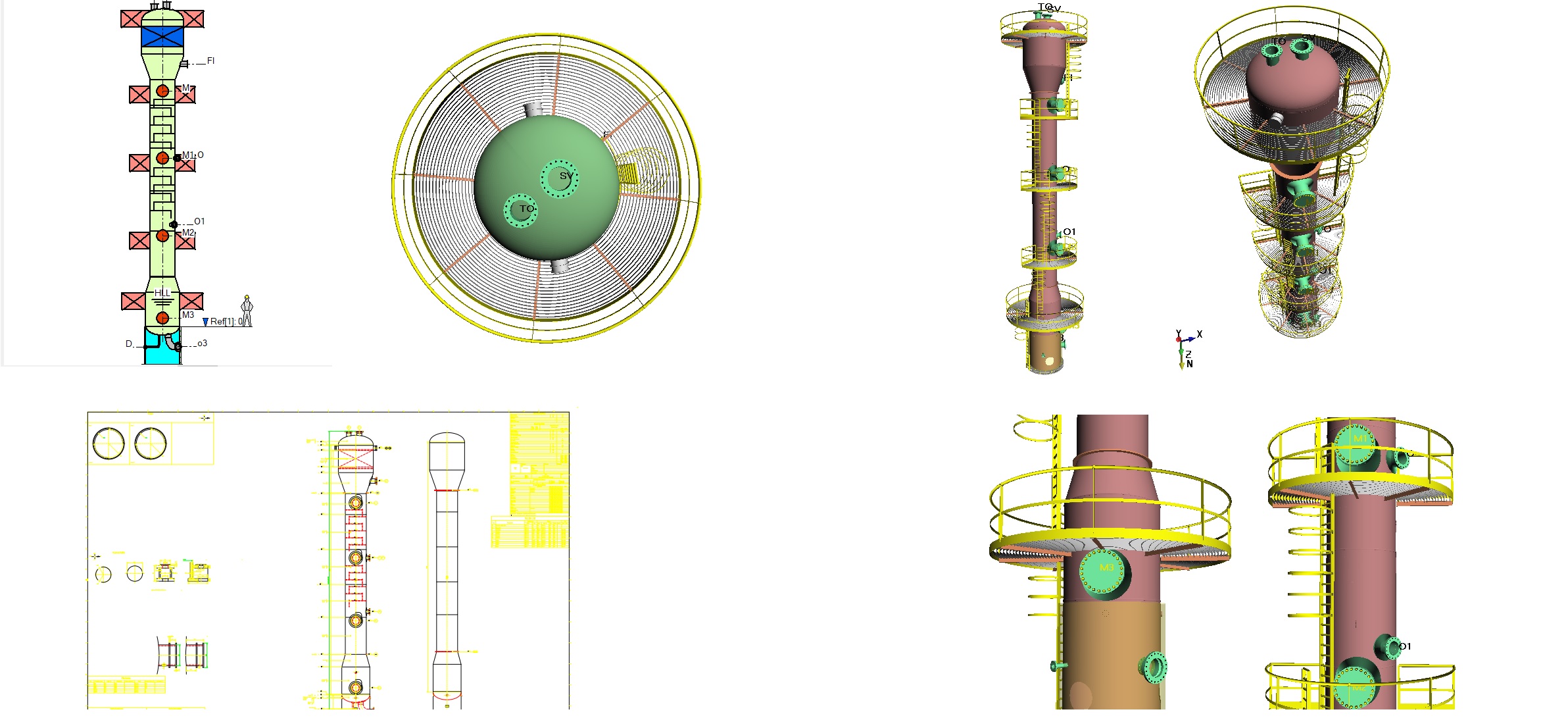
- Design of fluid storage tank
- Saddle and Skirt support vessels
- Thermo-mechanical analysis
- Spherical Pressure vessel design
- Vacuum filter design
- Multi-chambered pressure vessels
- Long distance pipelines
- Pipeline safe -span modelling
- Bills of material
- Generating Engineering design
- Vertical leg supported vessels
Project Showcase
Take a look at our featured projects
-
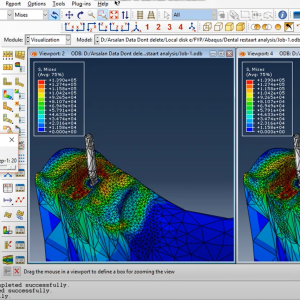
Drilling Jaw section in Abaqus
$ 150 -
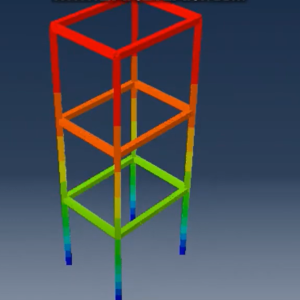
DESIGN OF SLIDING LEVER MECHANISM FOR REDUCING EARTHQUAKE ACCELERATION IN BUILDINGs USING ABAQUS
$ 150 -
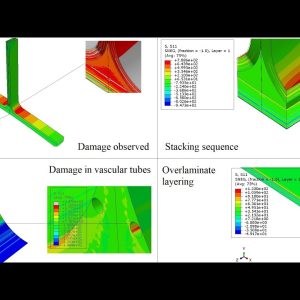
Thermo-Mechanical analysis and optimization of composite vascular T-joint using ABAQUS
$ 150 -
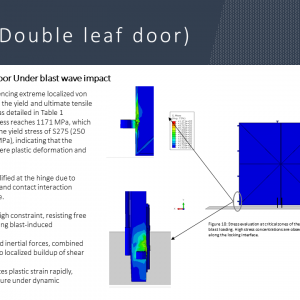
Evaluation of Structural Behavior of Steel Doors and its component Subjected to Air Blast Loading
$ 300 -
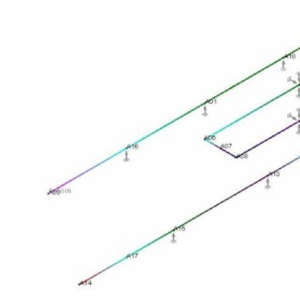
Modelling and Sagging Optimization of Pipeline Using Autopipe Under Gravity and Wind Load
$ 0 -
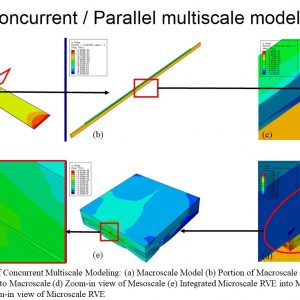
Concurrent vs Serial Multiscale Modelling of Intelligent MFC Composite CFRP-PZT (General Concept)
$ 200 -
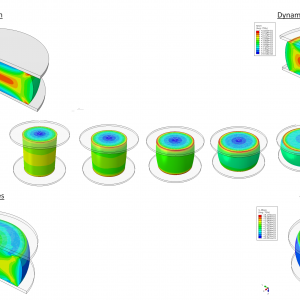
Modeling of Isothermal Deformation in Metals and Alloys Using Strain-Compensated Arrhenius Models via VUHARD Subroutine in ABAQUS (Gleeble Thermo-Mechanical Simulator
$ 500 -
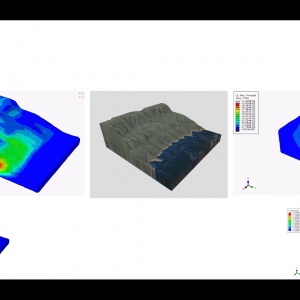
Numerical Simulation of Slope Stabilization With and Without GFRP Piles Based on Real Topographic Survey Data Using the Strength Reduction Method (SRM)
$ 200
We are a dynamic team of highly skilled engineers with diverse expertise across civil, mechanical, biomedical, and composite engineering. Our strength lies in using advanced computer-aided engineering (CAE) tools, such as FEA, CAD, and CFD, to solve complex real-world problems and deliver innovative, reliable, and cost-efficient solutions.
With extensive experience in structural design, fatigue life assessment, thermo-mechanical analysis, and product development, we support clients across multiple industries including aerospace, automotive, energy, healthcare, manufacturing, and infrastructure. From analyzing long-distance pipelines and pressure vessels to simulating biomedical implants and composite materials, we bring versatility and precision to every project.
We are proficient in a wide range of industry-standard software including ABAQUS, ANSYS, SOLIDWORKS, Creo, AutoCAD, XFLOW, TOSCA, and LabVIEW, enabling us to tackle projects of any scale or complexity. Our approach is driven by innovation, attention to detail, and a commitment to delivering measurable results that improve performance, reduce costs, and accelerate time-to-market.
What sets us apart is our ability to adapt and collaborate. Whether it’s designing next-generation biomedical devices, evaluating structural behavior in civil applications, or optimizing composite materials for advanced manufacturing, we partner with clients to provide solutions that are both technically sound and strategically valuable.
At our core, we are passionate about pushing the boundaries of engineering and turning challenges into opportunities. Our mission is simple: to help clients achieve success through engineering excellence.





