Modeling of Isothermal Deformation in Metals and Alloys Using Strain-Compensated Arrhenius Models via VUHARD Subroutine in ABAQUS (Gleeble Thermo-Mechanical Simulator
$ 500
The study focuses on modeling the isothermal deformation behavior of metals and alloys using the strain-compensated Arrhenius constitutive model within the VUHARD subroutine in ABAQUS, based on the Gleeble thermo-mechanical simulator.
Article followed and sited in video are as under:
Title: Study on hot deformation behavior of homogenized Mg-8.5Gd-4.5Y-0.8Zn-0.4Zr alloy using a combination of strain-compensated Arrhenius constitutive model and finite element simulation method
Doi# https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jma.2021.07.008
Title: Modeling and application of constitutive model considering the compensation of strain during hot deformation
Doi# https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.04.153
What this model can do?
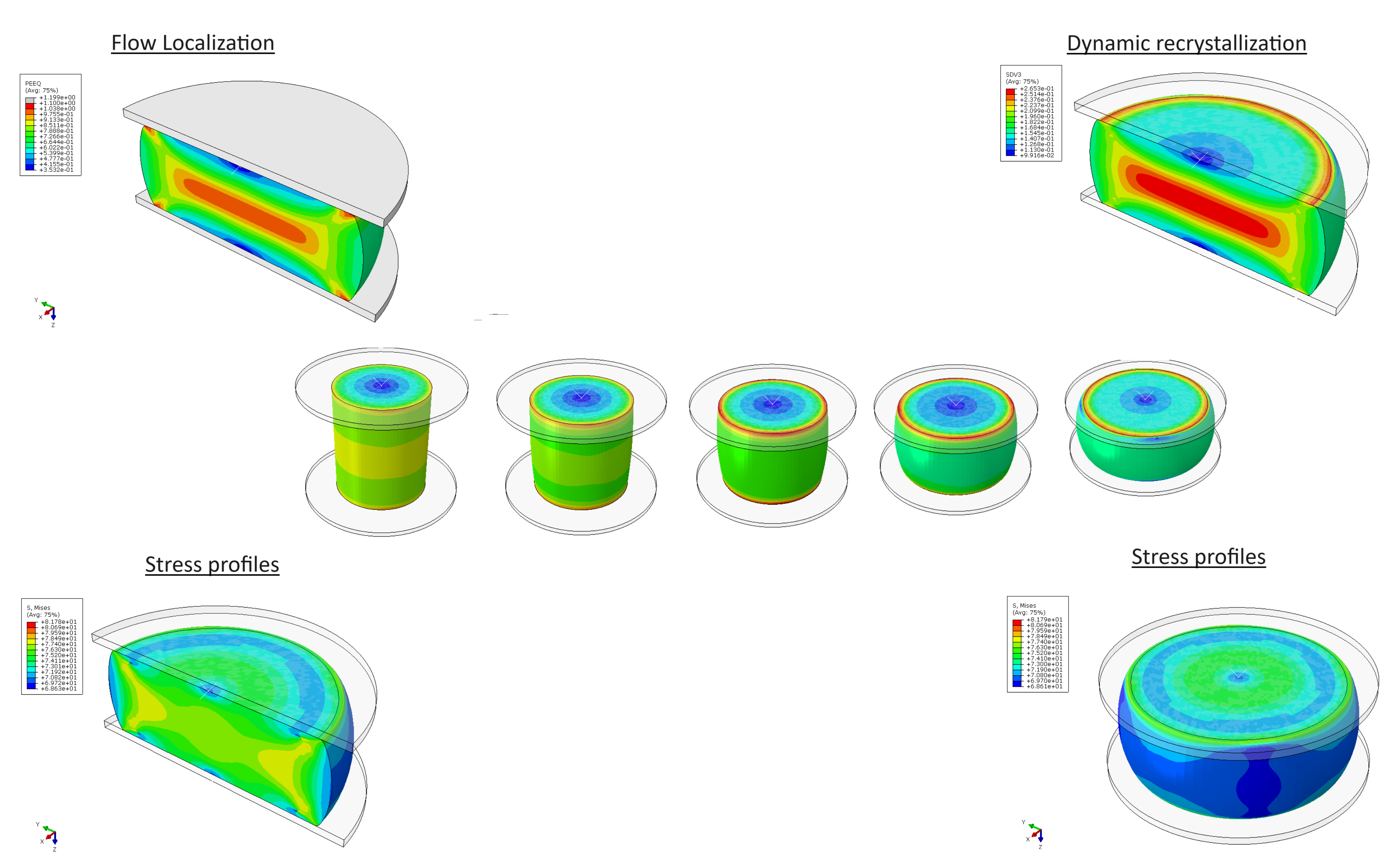
- Prediction of Flow Stress: The strain-compensated Arrhenius model allows for precise prediction of flow stress during hot deformation by considering the effects of strain, strain rate, and temperature simultaneously. This flow stress predictions allow manufacturers can adjust to adjust process parameter for the control of deformation processes such as forging, rolling, and extrusion.
- Dynamic Recrystallization (DRX) Modeling: The model integrates DRX kinetics, providing insights into microstructural evolution during deformation. This is critical for understanding grain refinement and mechanical properties enhancement during processes
- Numerical modelling: By incorporating the model into the ABAQUS VUHARD subroutine, it enables high-fidelity FEM simulations of complex deformation processes. This includes predicting temperature fields, stress distributions, and plastic strain, which are essential for optimizing industrial forming processes.
This strain-compensated Arrhenius model, implemented via the VUHARD subroutine in ABAQUS and validated through Gleeble simulations, represents a powerful tool for advancing the understanding and application of metal and alloy deformation processes
Access to Original Files
Our packages include comprehensive design documentation, detailed analysis reports, and essential files, all readily available for download. This collection ensures that you have everything needed to replicate the project or adapt it to fit your specific needs.
Project Customization
If you’d like to improve or modify our featured project to better suit your requirements, we offer customization services. This includes adjusting design parameters, adding extra analyses, or creating variations tailored to your industry or application.
Tutoring & Consultation
Receive expert guidance on complex engineering concepts through comprehensive tutorials and live sessions, designed to help you understand and apply these subjects effectively. Our expert-led tutorials provide a clear, step-by-step guide to complex engineering concepts.